Insights from VBeyond Corporation’s comprehensive survey on campus recruitment trends, Evolving Paradigms in Campus Recruitment: Insights and Strategies for Aligning Higher Education with Industry Demands, reveal a critical need for strategic higher education and academic industry partnerships. As the survey highlights, the dynamic landscape of campus placements is influenced by evolving student expectations, economic conditions, internship programs, and leadership development initiatives.
Moreover, the changing needs of employers have led to an increased focus on recruitment strategies and the role of staffing and recruitment services. This is aimed at enhancing student employability, ensuring that students are equipped with the skills that align with the demands of modern workplace.
This guide delves into practical strategies for educational institutions, businesses, and staffing service providers to enhance student employability, ensuring that graduates are well-prepared to meet the challenges of a competitive job market.
A. Empowering Institutions: Building Bridges Between Academia and Industry
Educational institutions hold the key to transforming academic knowledge into career-ready skills. By embedding practical experiences, forging academy-industry partnerships, and driving innovative programs, they can ensure students are well-equipped for the dynamic workforce.
1. Curriculum Integration
To effectively prepare students for the workforce, institutions must integrate practical experiences directly into the curriculum. This can be achieved through the following actions:
- Mandatory Internship Programs: Develop programs where internships are a required component of the degree. This ensures every student gains practical experience before graduation. Partner with local businesses to provide a range of internship opportunities.
- Project-Based Learning: Incorporate real-world projects into courses, allowing students to work on industry-relevant problems. Collaborate with companies to design these projects, ensuring they reflect current industry challenges.
- Co-Op Programs: Establish cooperative education programs where students alternate between classroom studies and working in their field of study. This not only provides practical experience but also allows students to apply their academic learning in real-time.
2. Industry Partnerships
Building and maintaining strong industry partnerships is crucial for enhancing student employability. Institutions can take the following steps:
- Advisory Boards: Create advisory boards with industry leaders who can provide insights into curriculum development, ensuring it aligns with industry needs. These boards can also help in identifying internship and job opportunities for students.
- Sponsored Research Projects: Encourage companies to sponsor research projects that involve students. This not only provides funding for the institution but also offers students the chance to work on real-world problems, gaining valuable experience and exposure.
- Industry Networking Events: Host regular networking events where students can meet and interact with industry professionals. These events can include career fairs, guest lectures, and panel discussions, providing students with opportunities to learn about industry trends and make professional connections.
In his transformative article A New Model for University-Industry Partnerships published by Harvard Business Review, Kenneth R. Lutchen articulates the necessity for dynamic and deep-seated collaborations between academic institutions and industry. He champions the concept of sustainable partnerships that are strategic and long-term, involving a consortium of companies actively participating on advisory boards. This model ensures that educational curricula evolve in tandem with rapid technological advancements and industry demands, rather than remaining static.
These advisory boards play a pivotal role in curriculum development by providing real-time industry insights, which help academic programs stay current and aligned with the latest technological trends. This continuous interaction fosters a curriculum that is both responsive and anticipatory of future industry needs, thereby enhancing the employability and readiness of graduates.
Highlighting successful implementations of this model, the article draws attention to Arizona State’s Polytechnic School and Boston University, where such partnerships have significantly boosted the relevance and effectiveness of their educational offerings. At Arizona State’s Polytechnic, industry advisory boards have directly influenced program updates and the integration of cutting-edge technologies into the curriculum, ensuring that students gain practical and relevant skills before entering the workforce. Similarly, at Boston University, the collaboration has led to the creation of state-of-the-art facilities and programs that prepare students to tackle real-world challenges effectively.
These schools have become exemplary in demonstrating how active collaboration with industry can transform educational outcomes. Students from these institutions are often seen as better prepared and more desirable by employers because of their firsthand experience with current technologies and methodologies. This preparedness not only enhances their immediate employability but also equips them with the adaptability required to thrive in rapidly changing industries and for leadership development ahead.
3. Career Services Enhancement
To support students in finding and securing internships and job placements, institutions should enhance their career services through the following actions:
- Dedicated Internship Coordinators: Hire coordinators specifically focused on developing and managing internship programs. These coordinators can build relationships with companies, assist students in finding internships, and ensure the quality of the internship experience.
- Career Counseling and Workshops: Offer personalized career counseling sessions to help students identify their career goals and develop action plans. Conduct workshops on resume writing, interview skills, and job search strategies to prepare students for the job market.
- Alumni Mentorship Programs: Connect current students with alumni working in their field of interest. Alumni can provide guidance, mentorship, and sometimes even internship or job opportunities, leveraging their industry connections.
4. Alumni Engagement
Engaging alumni can provide valuable resources for current students. Institutions can implement the following strategies:
- Alumni Networks and Portals: Develop online platforms where alumni can connect with current students, offer mentorship, and post job opportunities. These platforms can facilitate ongoing relationships between alumni and the institution.
- Alumni-Funded Internships: Encourage alumni to fund internship programs, especially for students who may face financial barriers to unpaid internships. This not only supports current students but also strengthens alumni ties to the institution.
- Alumni-Hosted Events: Organize events hosted by alumni where they share their career experiences and insights. These events can inspire students and provide practical advice on navigating the job market.
5. Innovative Programs and Initiatives
Institutions should continuously explore and implement innovative programs to enhance student employability. Examples of such initiatives include:
- Hackathons and Competitions: Organize hackathons and industry competitions where students can showcase their skills and work on real-world problems. These events can attract industry attention and lead to job offers.
- Virtual Internships: Develop virtual internship programs that allow students to gain experience with companies remotely. This expands opportunities for students who may not be able to relocate for internships.
- Micro-Internships: Implement micro-internship programs that offer short-term, project-based work experiences. These programs can provide students with diverse experiences and help them build a robust portfolio of work.
By integrating these comprehensive strategies, educational institutions can significantly enhance the employability of their students, ensuring they are well-prepared to thrive in a competitive job market.
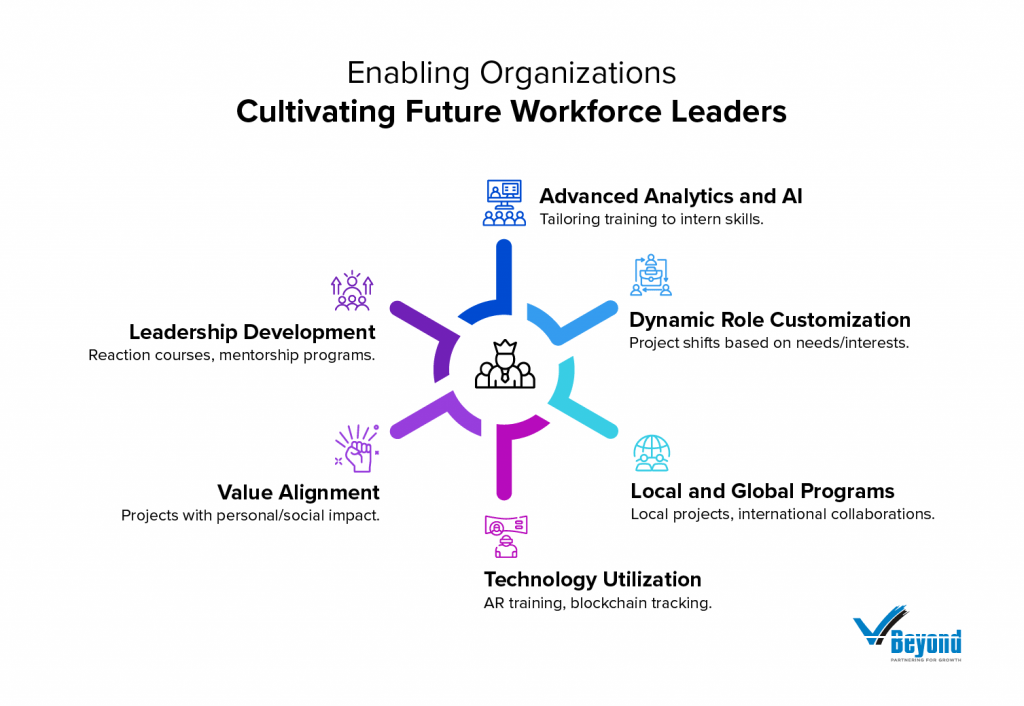
B. Enabling Organizations: Cultivating Future Workforce Leaders
This detailed approach to each strategy not only provides clarity and depth but also highlights how these approaches are practically implemented to benefit both interns and organizations, aligning with broader business strategies and goals.
1. Tailoring Training with Advanced Analytics and AI
Organizations increasingly leverage advanced analytics and artificial intelligence to enhance internship programs by adapting to the evolving competencies of interns. For example, tech startups might use AI systems to dynamically adjust the complexity of tasks in areas such as financial modeling or software development based on real-time performance assessments. This approach not only optimizes learning opportunities but also ensures that interns are constantly engaged and challenged at the right level.
The integration of such technologies presents challenges, particularly around data privacy and ethics. Organizations must develop robust data governance policies to ensure that intern data is handled securely and transparently, adhering to legal standards. Additionally, the use of proactive attrition modeling—an advanced form of predictive analytics—helps organizations forecast internship success rates and potential full-time conversions. This involves analyzing engagement metrics and performance data to identify interns who may need additional support or are likely candidates for full-time roles. Organizations can enhance the reliability of their predictive systems by regularly updating models with new data and correcting any biases identified in ongoing assessments.
2. Dynamic Role Customization
Modern organizations are developing systems that allow interns to shift between projects based on real-time business needs and personal interests. This approach, akin to an enhanced rotational program, provides interns with a variety of experiences, fostering adaptability and broadening their skill sets. For instance, an intern might start in a customer support role to understand user issues before transitioning to a product development team to address those needs directly.
Balancing dynamic project allocation with organizational goals can be complex. Implementing structured yet flexible project management frameworks can help align intern interests with strategic business needs, ensuring a beneficial outcome for both the interns and the organization.
3. Hyper-Localized and Global Development Programs
Organizations partner with local enterprises and startups to enable interns to work on projects that directly impact the local community. For instance, a consumer goods company might involve interns in developing eco-friendly packaging solutions in collaboration with local retailers. This approach not only gives interns the opportunity to see the immediate results of their efforts but also deeply engages them in meaningful work that benefits their community. Additionally, firms operating globally often create projects that require interns to collaborate across different international offices, enhancing their global acumen. For example, a multinational healthcare firm might have interns in both the U.S. and Germany collaborate on a project to enhance global patient data privacy protocols.
Local projects may face alignment issues among diverse local stakeholders, potentially leading to conflicts or stalled projects. To effectively address this, companies can establish a structured mediation process and clear communication guidelines. This framework helps in harmonizing goals and facilitates smoother project execution. Internationally, the primary challenge involves managing logistical issues such as time zone differences and cultural misunderstandings, which can impede workflow and affect productivity. Companies can mitigate these issues by implementing flexible work schedules and comprehensive cross-cultural training programs, ensuring all participants have a mutual understanding of work practices and cultural nuances.
Continuing in this detailed manner ensures that each strategy is explained comprehensively, addressing real-world applications, potential challenges, and practical solutions to maintain a consistent narrative across the section.
4. Advanced Technology Utilization for Training and Evaluation
- Customized AR Training Modules: Companies across various industries, such as construction and healthcare, are turning to augmented reality (AR) to create customized, immersive training modules tailored to each intern’s learning curve and project requirements. For example, a construction firm might use AR to simulate complex building scenarios, allowing interns to navigate through architectural challenges and make structural adjustments in a controlled, risk-free environment. This method significantly enhances the learning process by providing a deep understanding of complex systems through interactive experiences.
A major challenge with AR technology is the high cost associated with its development and maintenance. To address this, companies can form partnerships with AR technology providers, which can reduce costs through shared development and subscription-based models. Additionally, investing in scalable AR solutions that can be adapted for different training needs and updated with new content can ensure long-term viability and cost-effectiveness.
- Blockchain-Based Achievement Tracking: Innovative firms, especially in sectors requiring high levels of documentation like finance and legal, are adopting blockchain technology to track and verify all intern activities and evaluations securely. This approach provides a transparent and immutable ledger of an intern’s contributions and skills, which can be referenced in future career opportunities within or outside the organization.
Integrating blockchain into existing IT systems poses technical and cost-related challenges. Companies can overcome these hurdles by initiating pilot projects to evaluate the impact and scalability of blockchain solutions before full-scale implementation. Collaborating with experienced blockchain service providers can also streamline the integration process, ensuring a smooth transition and effective operation.
5. Generational Value Alignment
Organizations are creating internal marketplaces where interns can select projects not just based on skill or career path but also aligning with their personal values and social impact goals. This approach is particularly evident in firms focusing on sustainability and social responsibility, where interns can choose to work on initiatives that promote environmental conservation or community development, thus aligning their personal passions with professional experiences.
The challenge lies in balancing intern preferences with the strategic goals of the organization to ensure the viability of projects. Companies can address this by employing AI-driven tools that match interns to projects based on a combination of their skills, career aspirations, and personal values. Regular feedback loops and project evaluations can further align outcomes with both intern satisfaction and organizational objectives.
6. Enhanced Leadership Development
A key tool in this category is leadership reaction courses. Adapted from military training programs, these courses are tailored to the corporate environment to cultivate key leadership skills such as teamwork, problem-solving, and adaptability under pressure. For example, a technology firm might simulate scenarios like network failures or cybersecurity breaches, requiring interns to make quick, effective decisions in stressful situations. These exercises are designed to test leadership qualities in real-world equivalent conditions, preparing interns for future roles that require high-level decision-making and crisis management.
The primary challenge with these intensive training programs is ensuring they are accessible and beneficial to all interns, regardless of their background or physical ability. To make these leadership development programs inclusive, companies can customize scenarios to accommodate a wide range of capabilities and provide alternative learning tracks that ensure no intern is disadvantaged. Regular mentorship and detailed feedback sessions can help reinforce learning outcomes, ensuring interns gain the most from their training experiences.
C. Recruitment Strategies for Bridging the Gap: Enhancing Student Employability Through Staffing and Recruitment Services
As the job market evolves, staffing and recruitment services play a pivotal role in shaping the future workforce. Here, we explore cutting-edge recruitment strategies that enhance student employability and seamlessly align educational achievements with industry demands.
1. Predictive Analytics Integration for Skill Gap Analysis
Staffing and recruitment services can leverage predictive analytics to identify emerging skill gaps in various industries proactively. This advanced approach allows them to advise educational institutions on necessary curriculum adjustments or to develop specialized training programs that anticipate future market demands.
Balancing the predictive insights with current market demands can be tricky. Services can address this by using a combination of historical data, current job market trends, and predictive modeling to provide well-rounded recommendations to educational partners and candidates.
2. Micro-Internship Platforms
Developing platforms that offer micro-internships—short, professional assignments that are project-based—can help students gain real-world experience in various industries without the long-term commitment of traditional internships. This is particularly beneficial for exploring different career paths and gaining diverse experiences quickly.
The challenge lies in structuring these micro-internships to provide meaningful learning experiences rather than just short-term work solutions. Staffing services can collaborate with companies to ensure that each micro-internship has clear learning objectives and outcomes, making these opportunities both practical and educational.
3. Virtual Reality (VR) Internship Simulations
Staffing firms can incorporate VR technology to simulate real-work environments and scenarios for internship candidates, allowing them to gain practical experience in a controlled, risk-free setting. This technology can be particularly useful in fields where on-the-job training might be hazardous or logistically challenging to arrange.
High costs and technological demands are the main challenges of implementing VR training. Staffing firms can partner with VR technology providers and seek grants or subsidies designed to support innovative training solutions to mitigate these challenges.
4. Continuous Professional Development Subscriptions
Offering subscriptions for continuous professional development, tailored to specific career paths, can help internship candidates stay ahead in their chosen fields. These can include access to up-to-date courses, webinars, and exclusive content that keeps them informed of the latest industry changes and developments.
Keeping the content engaging and relevant over time can be challenging. Regular updates, feedback systems, and collaborations with industry experts can help ensure the resources remain valuable and appealing.
5. Advice for Internship Candidates
To make the most of their internship, candidates should follow these key strategies for a productive and enriching experience.
Maximizing Your Internship Experience:
- Be Proactive: Take initiative to seek out additional responsibilities and express interest in various projects. Showing eagerness and enthusiasm can make a significant impression.
- Network Intensively: Use the opportunity to build connections with professionals within and outside the department. Networking can provide valuable insights and open doors to future job opportunities.
- Set Clear Goals: Start your internship with clear objectives in terms of what you want to learn and achieve. Discuss these goals with your mentor or supervisor early on to align your activities with these objectives.
- Request Feedback Regularly: Regular feedback is crucial for improvement. Ask for constructive criticism and advice frequently, and use it to enhance your skills and professional demeanor.
- Reflect on Your Experience: Keep a journal of your daily experiences and challenges. Reflecting on what you’ve learned and areas for improvement can enhance your professional growth and prepare you for future opportunities.
By incorporating these advanced strategies and providing tailored advice, staffing and recruitment services can significantly enhance the value they offer to both educational institutions and internship candidates, effectively bridging the gap between academic preparation and industry needs.
Conclusion
Enhancing student employability requires a holistic approach where educational institutions, organizations, staffing and recruitment services collaborate seamlessly. This means bridging the gap between academic learning and real-world application, aligning educational outcomes with industry needs, and leveraging unique recruitment strategies. Additionally, raising candidate awareness about proactive career planning and continuous skill development is crucial for sustaining employability in a rapidly changing job market. These elements need to work in tandem; only then can we create a future-ready workforce poised to drive innovation and excel in the global economy.
Ready to bridge the gap between education and employment? Partner with us today to create tailored internship programs and build a future-ready workforce. Contact VBeyond to learn how our staffing and recruitment services can help you cultivate top talent.


